Connecting to a Windows VM via RDP through a Linux Bastion Host port forwarding on CODE-DE
Connecting to Windows virtual machines using Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) often requires exposing the RDP service directly to the public network. This approach increases the attack surface, makes the service more visible to automated scans, and may conflict with security policies that restrict direct access to management ports.
A common way to address these limitations is to avoid publishing the RDP service altogether and instead route the connection through a controlled entry point. In this setup, a Linux virtual machine acts as a bastion host, and the RDP traffic is tunneled through an encrypted SSH connection.
The bastion host does not establish an RDP session itself. It only forwards TCP traffic using SSH port forwarding. From the Windows VM perspective, there is exactly one incoming RDP connection, originating from the local machine through the SSH tunnel. The Windows VM is not connecting to itself, and no additional RDP sessions are created by the bastion host.
This setup reduces exposure, improves overall security, and enables the use of a single floating IP address to access multiple Windows virtual machines without assigning public IP addresses to each of them.
What we are going to cover
Prerequisites
No. 1 Account
You need a CODE-DE hosting account with access to the Horizon interface: https://cloud.fra1-1.cloudferro.com/auth/login/?next=/.
No. 2 Virtual machines
Create the following virtual machines in the same CODE-DE cloud project:
One Linux VM (Ubuntu 24.04) acting as the bastion host, with SSH access enabled.
One Windows VM (Windows Server 2019) acting as the RDP target, located in the same private network as the bastion host.
Assign a public IPv4 address only to the Linux bastion host. The Windows VM does not require a public IP address, as it will be accessed exclusively through SSH port forwarding via the bastion host.
The following articles may serve as a reference:
How to create a Linux VM and access it from Windows desktop on CODE-DE
How to create a Linux VM and access it from Linux command line on CODE-DE
The two virtual machines used in this article are shown below: Bastion running Ubuntu 24.04 and rdp running Windows Server 2019.
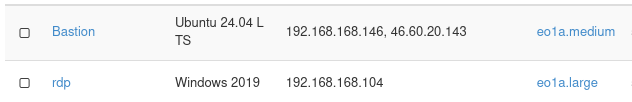
No. 3 Local Windows system
You will perform all steps in this article from a local Windows 11 system.
No. 4 Security groups
Ensure that the following ports are allowed by the security groups assigned to your virtual machines:
22/tcp — SSH access to the Linux bastion host
3389/tcp — RDP access inside the private network (between the bastion host and the Windows VM)
Your VMs should be assigned a security group similar to allow_ping_ssh_icmp_rdp.
No. 5 PuTTY and SSH key
Install PuTTY on your local Windows system if it is not already available:
You also need:
The private SSH key downloaded from the OpenStack dashboard
The key converted from .pem to .ppk format using PuTTYgen
For detailed instructions, see: How to access a VM from Windows PuTTY on CODE-DE
No. 6 Windows Administrator credentials
The Administrator password for the Windows VM is set inside the virtual machine itself.
Use the Console option in the OpenStack dashboard to log in to the Windows VM and set or change the Administrator password before attempting the RDP connection.
The Administrator password is required for RDP authentication and is unrelated to any local Windows users or SSH accounts used in this article.
Step 1. Information required to establish connection with the bastion host
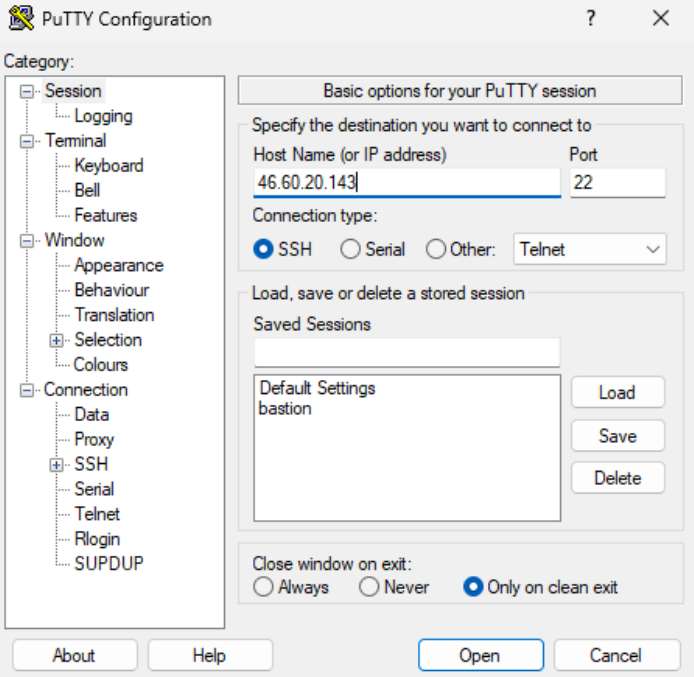
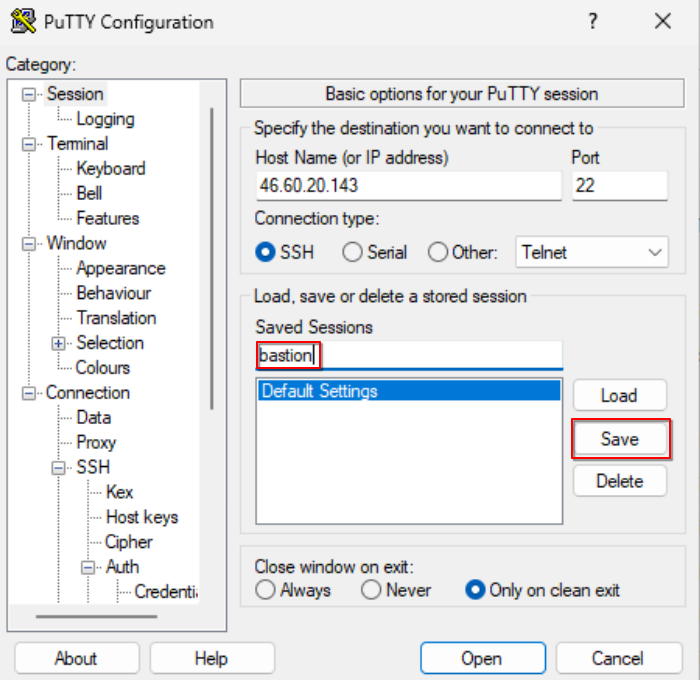
Launch PuTTY and change the settings according to the instructions:
Session tab: Provide the host (bastion) floating IP address and the SSH port (default 22).
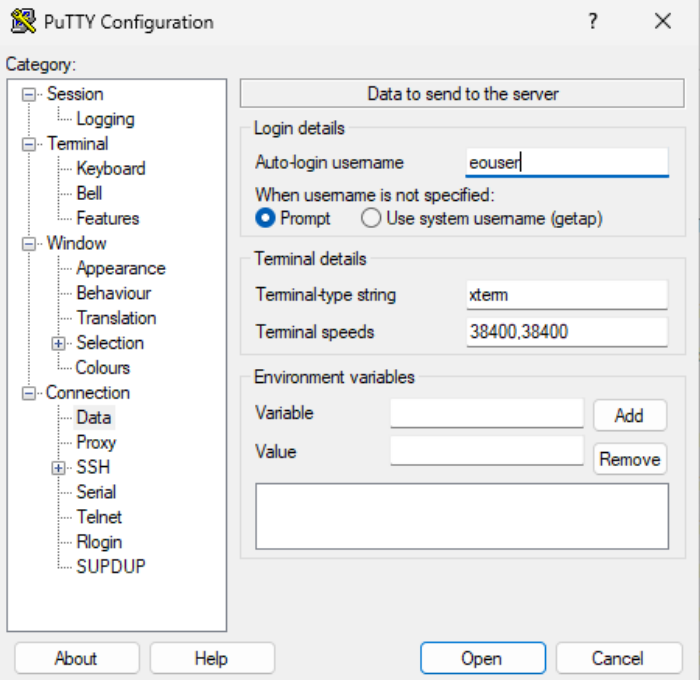
Connection > Data tab: Set auto-login username as “eouser”.
Now select Connection > SSH > Auth > Credentials > Private key file for authentication: and add the private key in the .ppk format.
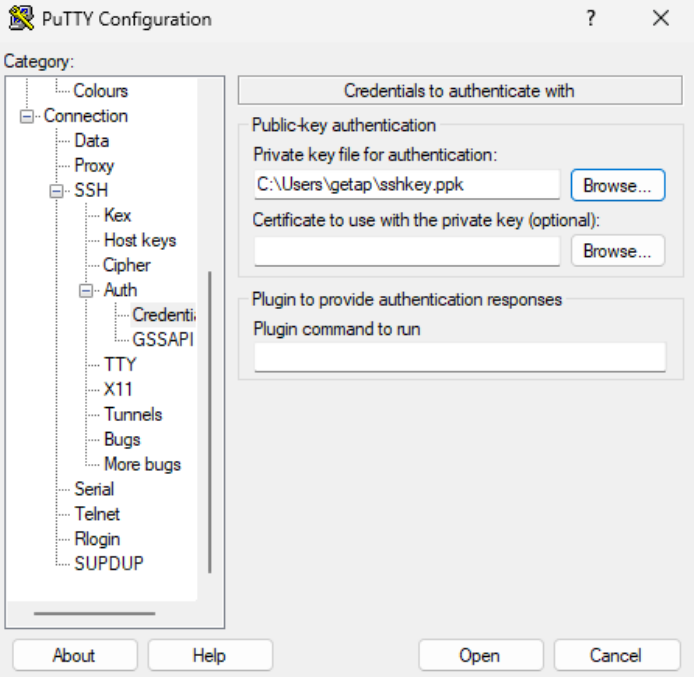
Connection > SSH > Tunnels: Provide the source port for the localhost RDP connection and destination (in the following format: private IP address of Windows VM:RDP port - as seen on the screenshot below).
Click the “Add” button to confirm the changes. Your forwarded port should now be visible in the upper tab.
Provide the name of the session and save your config to avoid repeating the whole process every time you would like to connect to your instance again.
Step 2. Open connection in PuTTy
Click “Open” to establish the connection:
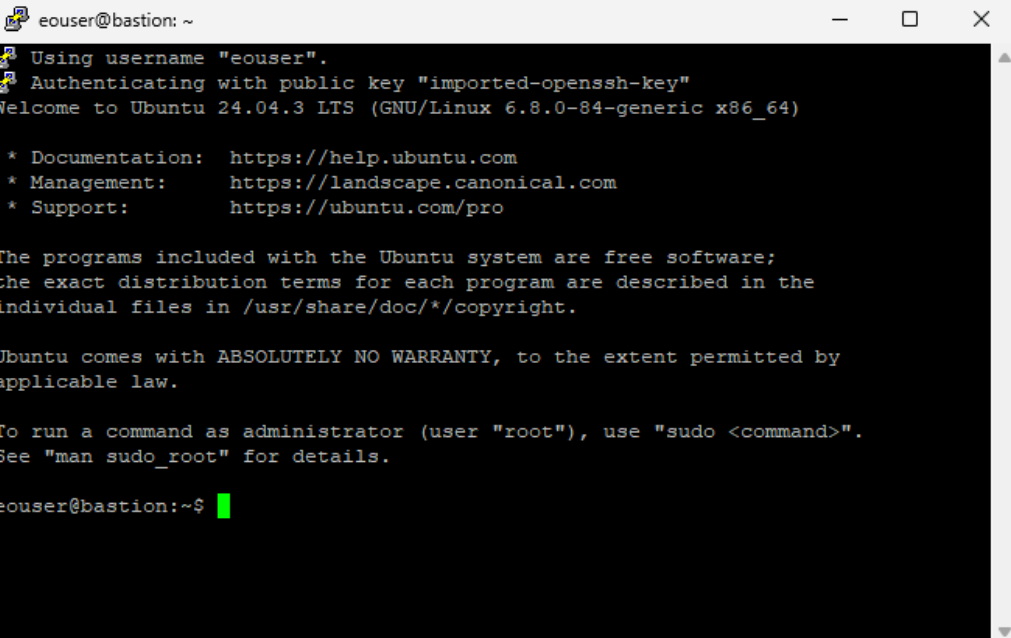
The end result: you are now acting as eouser on bastion VM, on Linux. Leave the PuTTY session open while using RDP, as it maintains the SSH tunnel required for the connection.
Step 3. Start an RDP session to localhost to reach the destination server
This step is performed on your local Windows system, not on the bastion host.
Keep the PuTTY SSH session open, as it maintains the SSH tunnel and port forwarding. Closing PuTTY will immediately terminate the tunnel and disconnect the RDP session.
On your local Windows machine, start the Remote Desktop client:
Press Win + R.
Type
mstscand press Enter to open Remote Desktop Connection.
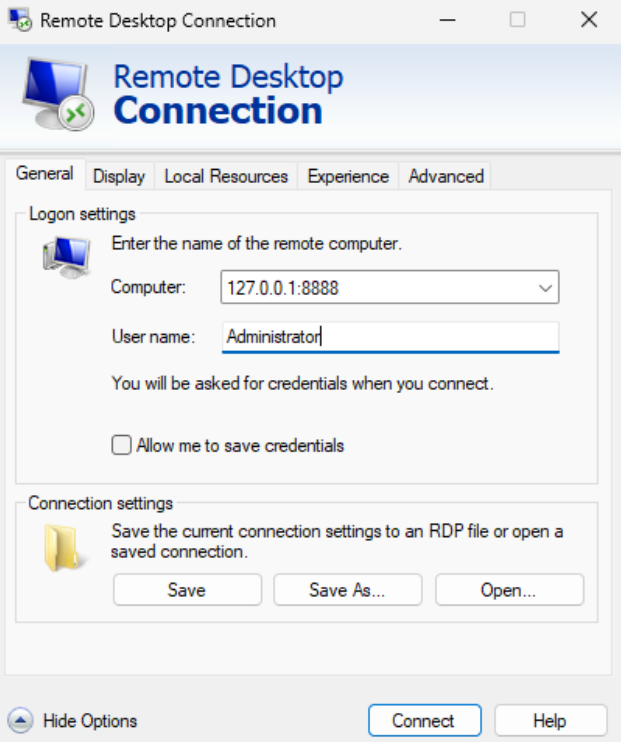
In the Computer field, enter the forwarded local address and port configured in PuTTY (for example
localhost:8888or127.0.0.1:8888).Click Connect.
When prompted for credentials, enter:
Username:
AdministratorPassword: the Administrator password set for the remote Windows VM using the OpenStack dashboard console (see Prerequisite No. 6).
Important
If RDP authentication fails and no “Reset Password” option is available in Horizon, open the Console for the Windows VM and verify or change the Administrator password there.
Confirm the certificate warning if prompted to proceed with the connection.
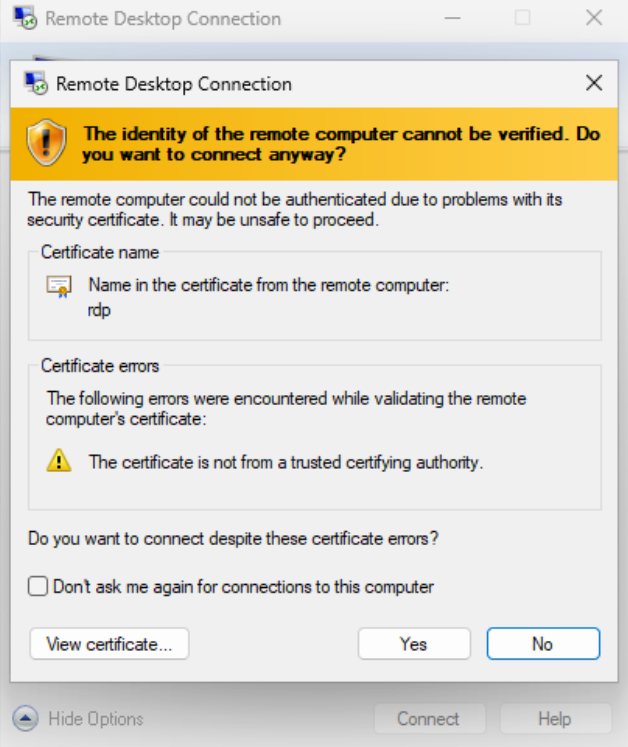
After successful authentication, you are now connected to the remote Windows VM through the SSH tunnel provided by the Linux bastion host.
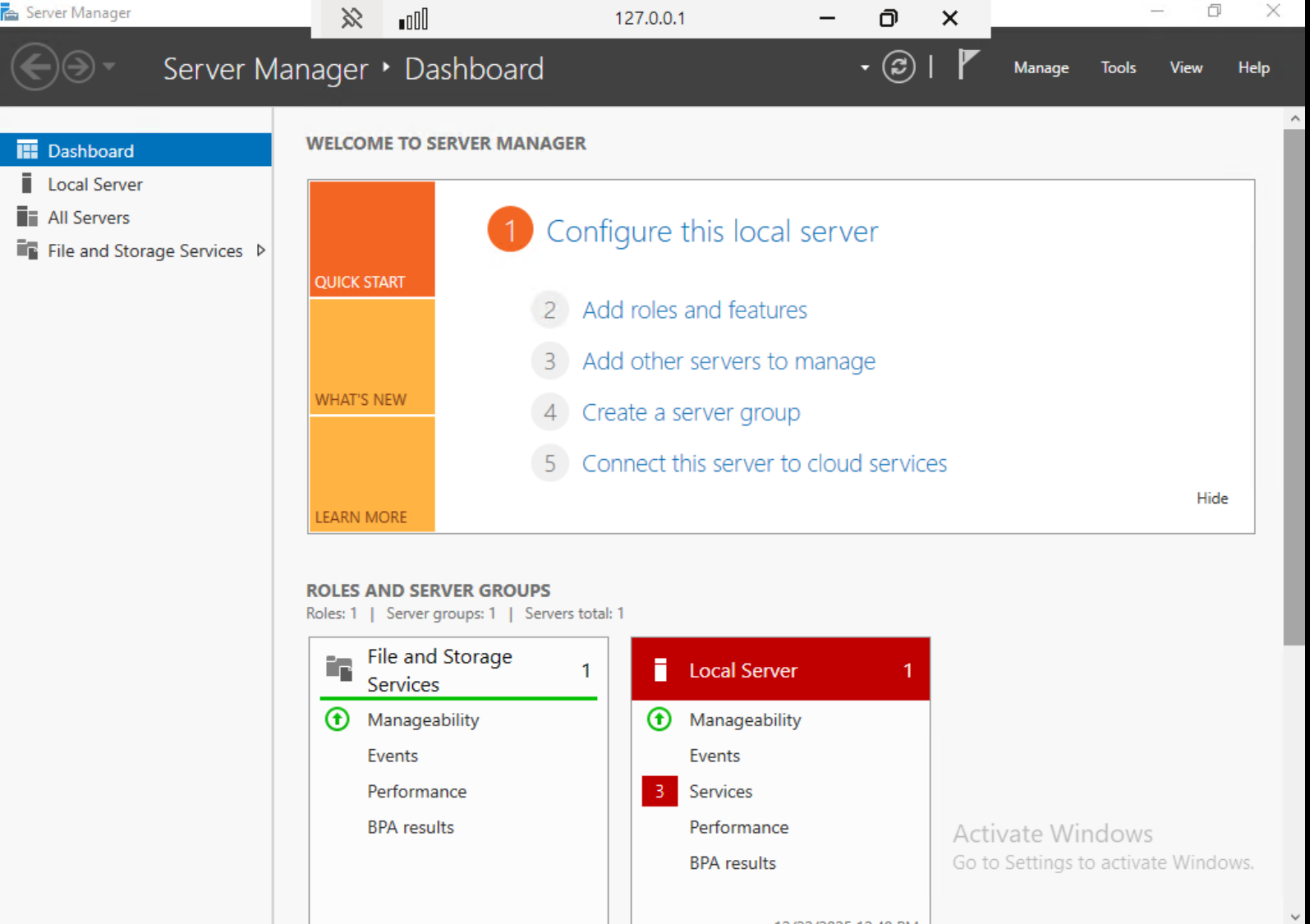
Local Windows 11 vs. remote Windows Server
At this stage, the RDP connection is active and you are working on the remote Windows Server virtual machine, not on your local Windows 11 system.
Although the RDP client was started locally and the connection target was specified as localhost:8888, this address represents only the local end of the SSH tunnel. The Windows session itself runs entirely on the remote Windows Server VM, and all authentication and system behavior are handled there.
The Server Manager dashboard confirms this state. Server Manager is available only on Windows Server editions and indicates that all further actions apply exclusively to the remote server. The local Windows system is used only to maintain the SSH tunnel and display the remote desktop.
How many RDP connections can you have at one time
Windows operating systems (including Windows Server 2019 used here, as well as Windows 10 and Windows 11) allow only one interactive RDP session per user account at a time by default.
If a second RDP connection is initiated using the same user while an existing session is still active, Windows will automatically disconnect the previous session and display a message such as:
“You have been disconnected because another connection was made to the remote computer.”
This behavior is expected and not related to SSH port forwarding or the Linux bastion host.
If you are unexpectedly disconnected after connecting, verify that no other RDP client is already connected to the same Windows VM using the same user account.
Using one bastion host to access multiple Windows VMs
A single Linux bastion host can be used to access multiple Windows virtual machines at the same time, provided that all Windows VMs are connected to the same private network and are reachable from the bastion host.
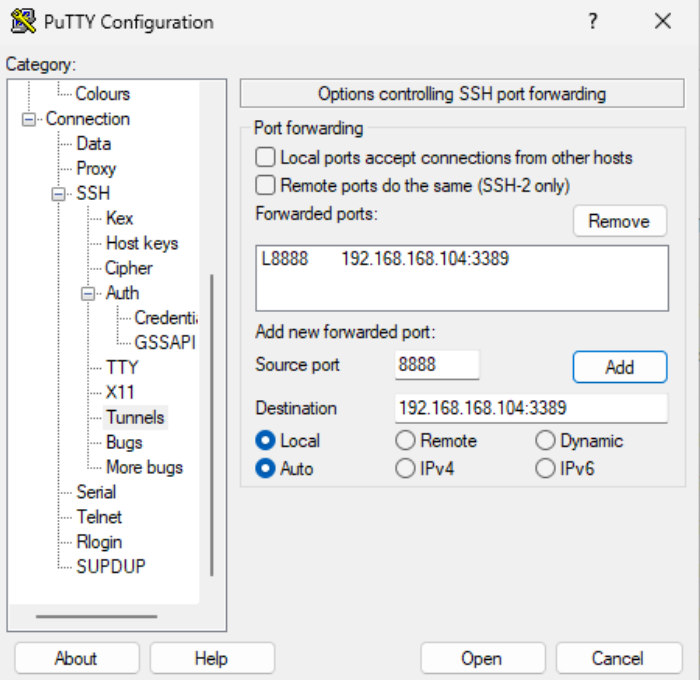
Each Windows VM continues to listen on the standard RDP port (3389) internally. On the local Windows system, separate SSH port forwardings are created, each using a different local port and pointing to a different Windows VM.
For example:
localhost:8888→192.168.168.104:3389(Windows VM 1)
localhost:8889→192.168.168.105:3389(Windows VM 2)
These port forwardings can be configured either as separate saved PuTTY sessions or as multiple tunnel entries within a single PuTTY session. Each RDP connection is then initiated independently using mstsc and the corresponding local port.
This approach allows you to reuse one bastion host and one floating IP address to securely access multiple Windows systems in parallel, while keeping all Windows VMs free of public IP addresses and maintaining a consistent security model across the project. In PuTTY, each forwarded port is defined under Connection > SSH > Tunnels, using a unique local source port.
Secure access to Windows VMs in private networks
By completing this procedure, you have configured RDP access to a Windows virtual machine without exposing the RDP service to the public network. The Windows VM remains accessible only inside the private network, while all external access is routed through a Linux bastion host using an SSH tunnel.
This access model is commonly used on CODE-DE platforms where Windows virtual machines are part of private project networks and direct access to management services is restricted. Typical use cases include Windows-based applications that operate on EODATA, object storage, or other internal services available only within the project network.
The bastion host acts as a single entry point for administrative access. Additional Windows VMs can be accessed using the same bastion host by configuring separate SSH port forwardings, allowing multiple private Windows systems to be managed without assigning public IP addresses to each of them.
In this setup, the Linux bastion host provides controlled network access, while Windows VMs remain isolated within the private project network.