How to create a Linux VM and access it from Windows desktop on CODE-DE
Step 1: Login into your account
Use the standard link for https://administration.code-de.org/login webpage.
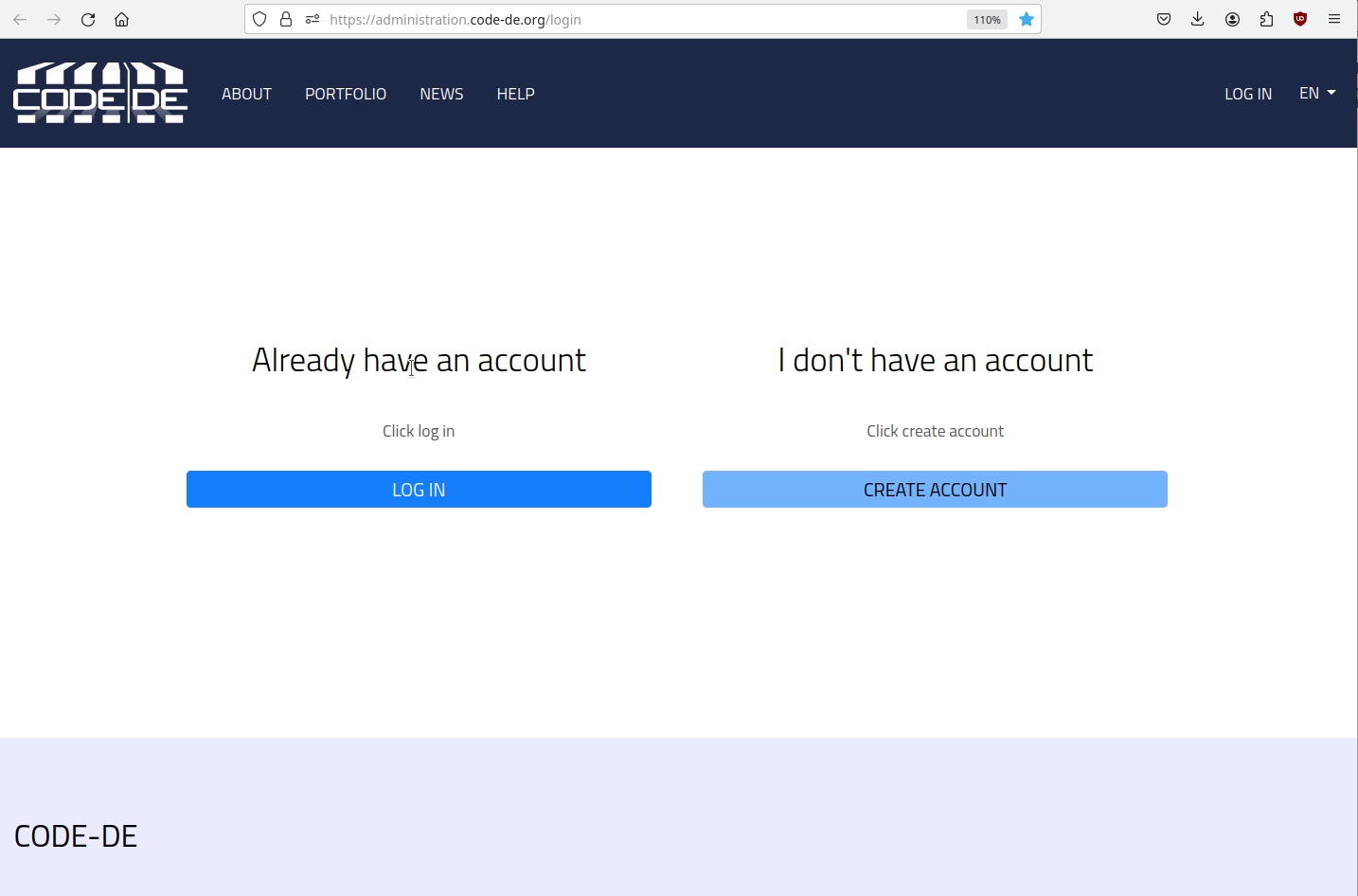
Step 2: Log into Horizon
On the left bottom side, you can find Management Interfaces, choose FRA1-1 Horizon.

In another one logging step choose CODE-DE and use the same credentials as before.
The second option is Keystone Credentials, if you want to use this option, you have to know your domain. (as below)
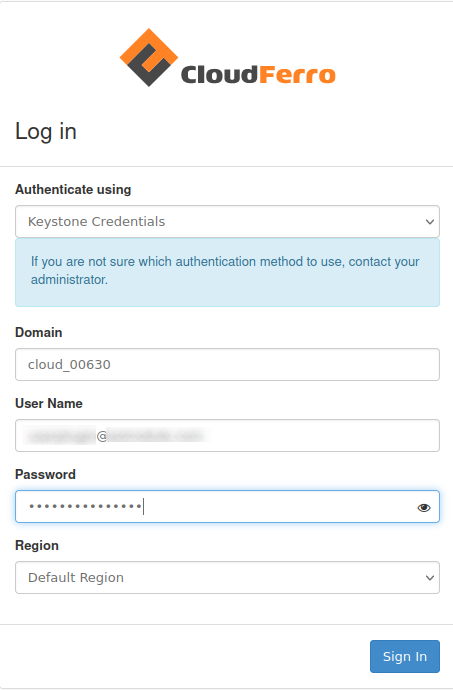
HOW TO FIND THE DOMAIN:
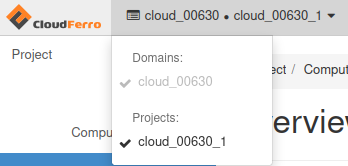
On top right, near the CloudFerro Logo you’ll find your domain name and project that you are recently using. You can create new projects and switch between them.
After you’ve successfully logged in, you may start creating your Linux instance.
Step 3: Create a new Linux instance in Horizon
Go to Compute → Instances and click Launch Instance.
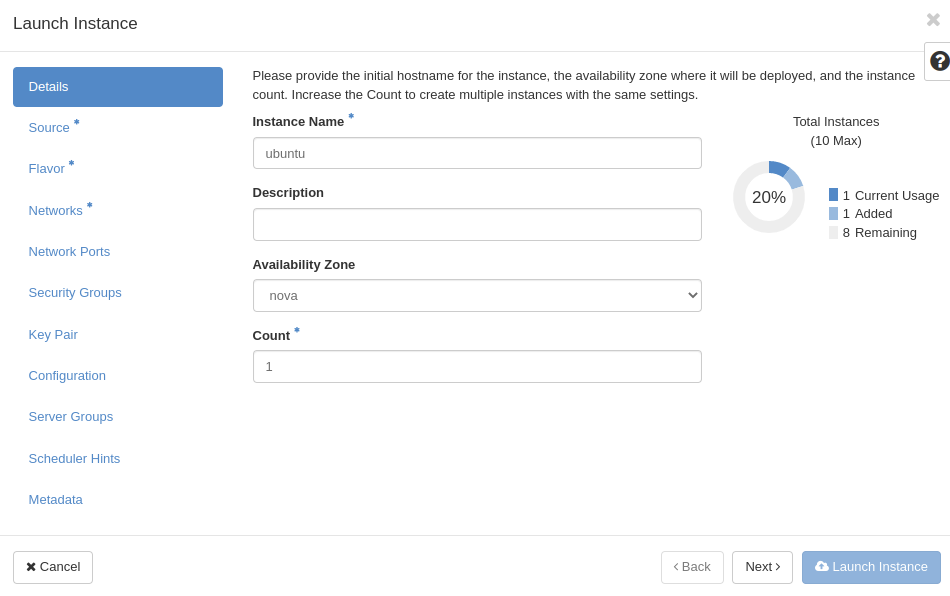
In Details tab type Name of your instance and then click Next.
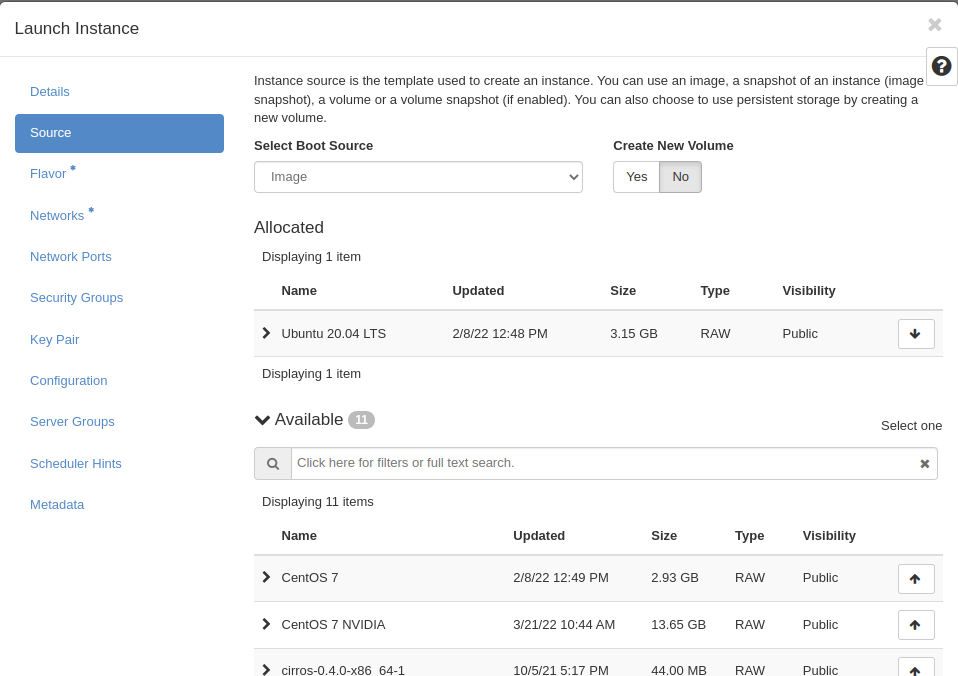
After that, you need to choose the source of your instance. Click one of the up arrows on the right side and allocate one of the following.
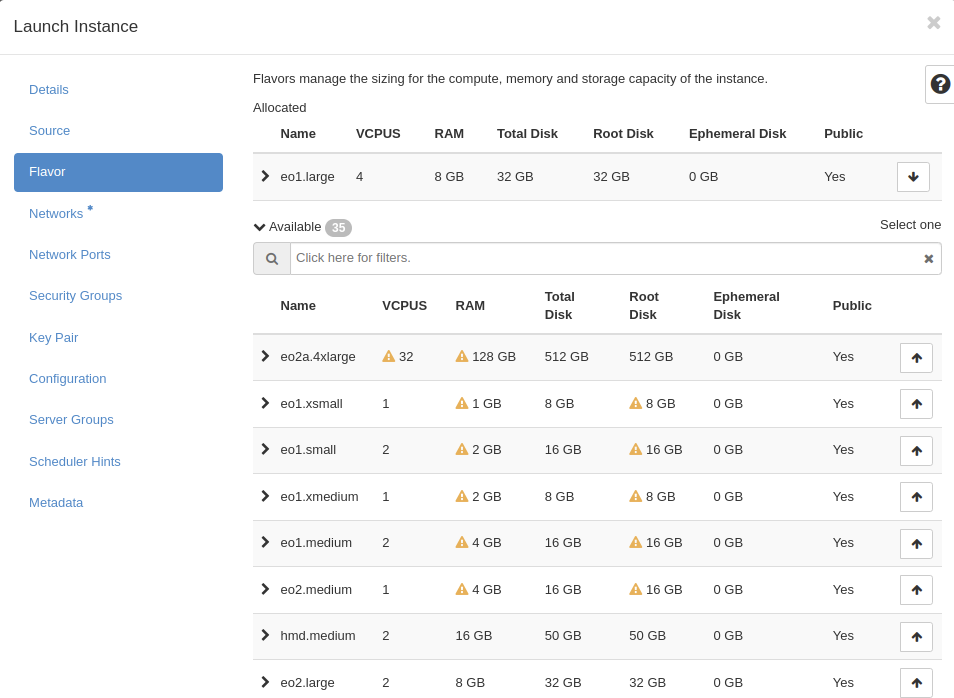
In flavor tab choose one of the available flavours, like step before. If you see yellow warning on flavour you are not able to use this flavour.
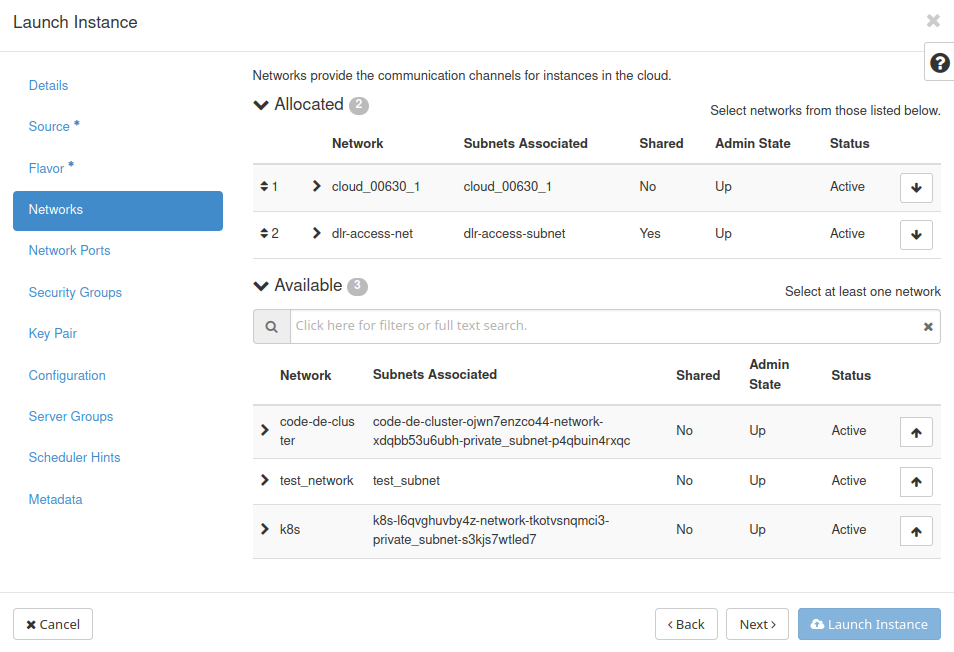
In next tab choose dlr-access-net network, which gives you access to earth pictures. Also, add network called cloud_xxxx, which is the default network created with your project.
You can also create your own network in Main Network tab.
If you want to run services or use specified protocols, first you must allocate security groups. Choose two security groups, one called default and other one called cloud_XXXXX_1. They regulate the following ports:
default
ALLOW IPv6 to ::/0
ALLOW IPv4 to 0.0.0.0/0
ALLOW IPv4 from default
ALLOW IPv6 from default
cloud_00630_1
ALLOW IPv4 icmp from 0.0.0.0/0
ALLOW IPv4 22/tcp from 0.0.0.0/0
ALLOW IPv6 to ::/0
ALLOW IPv4 to 0.0.0.0/0
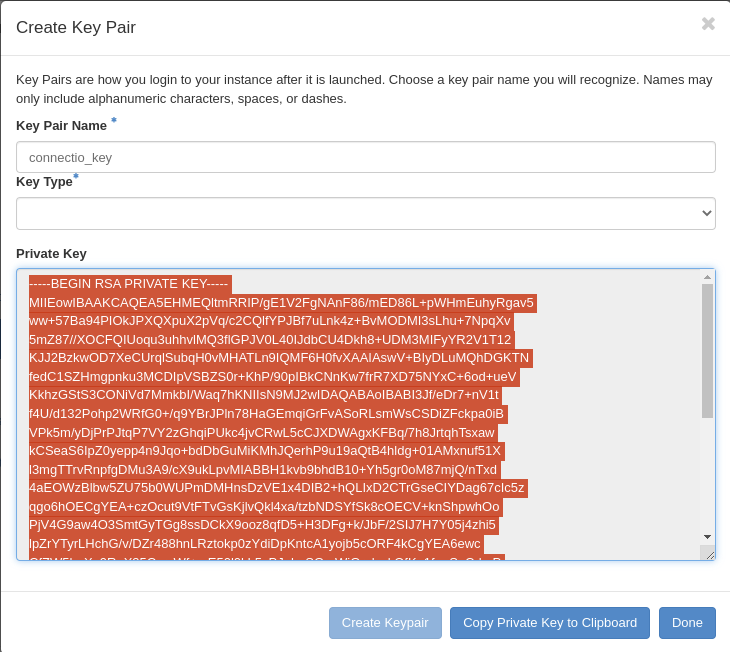
A very important thing is to create or import SSH key, it is necessary to connect to your VM via SSH. Create your key and save your private key wherever you want.
Now you can click launch Instance and wait several minutes to launch it right.
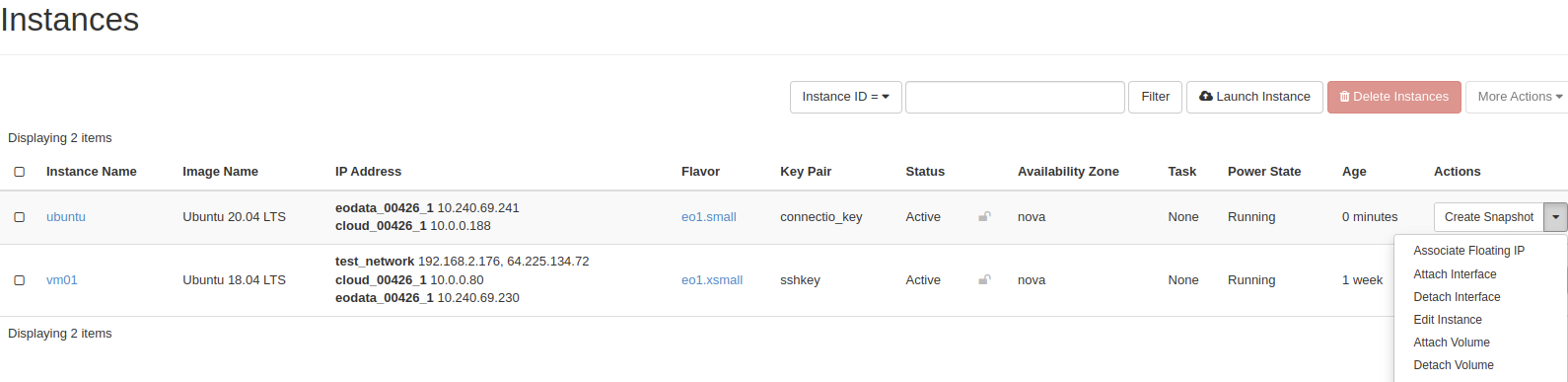
When our instance is working we must Allocate Floating IP (public IP) to it, after this step your VM should be able to connect from other space.
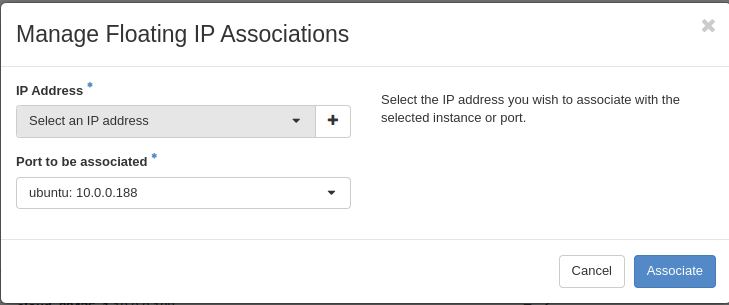
To allocate floating IP you must click “+” (plus) next to Select an IP address. You must also select interface please do not select eodata interface.
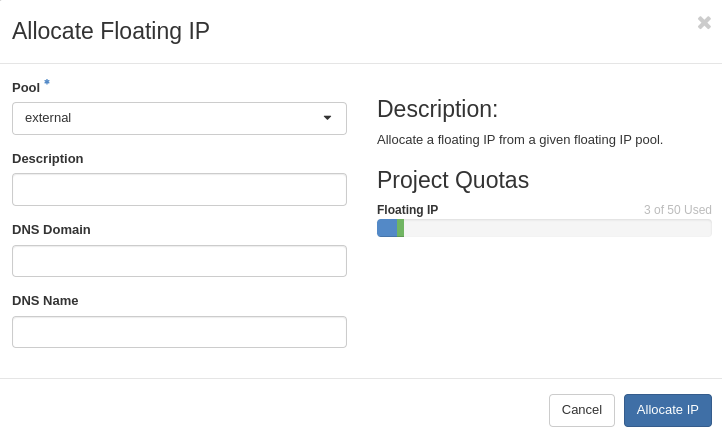
Choose Pool external and click Allocate IP
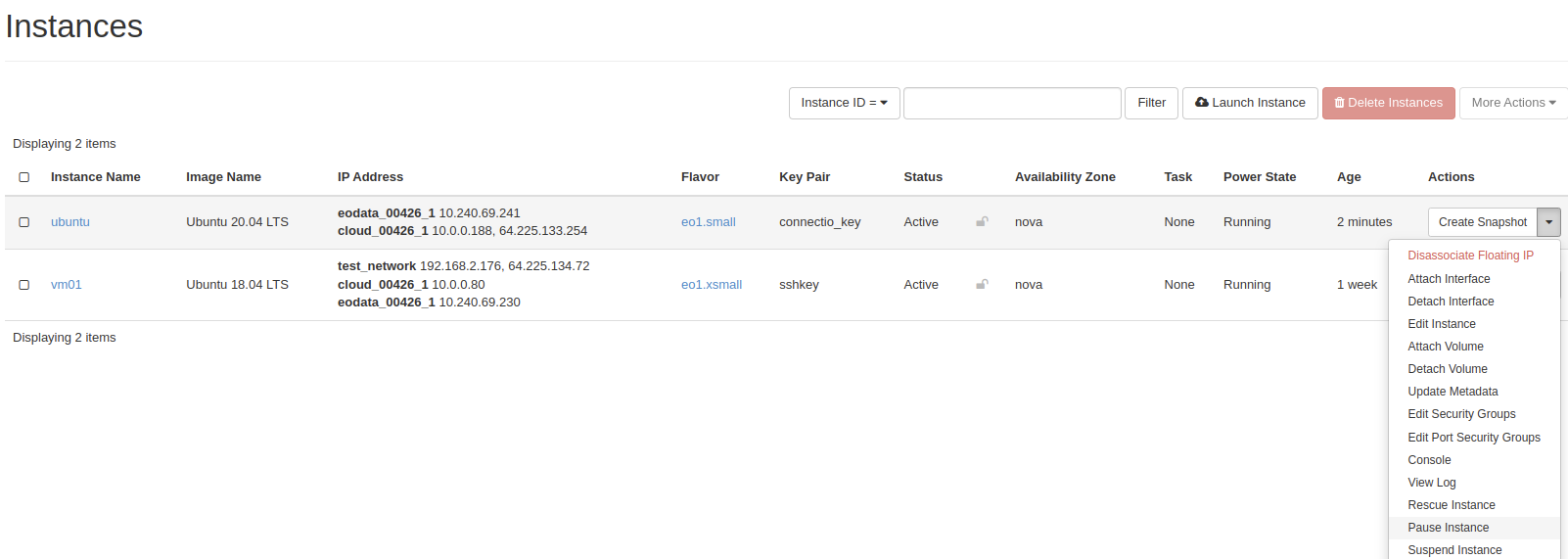
If everything is right you should see public address next to your cloud_xxx network, you can also use console that is implemented in openStack, open pull down menu and choose Console, you can log into it with eoconsole account, but in the beginning you must change password.
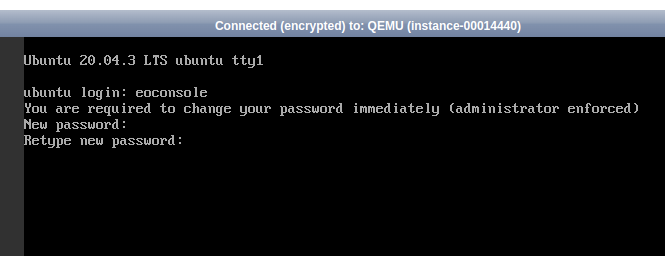
Please be informed that some of common operations like: copying (ctrl+c), pasting (ctrl+v) etc. are not being supported inside the console window.
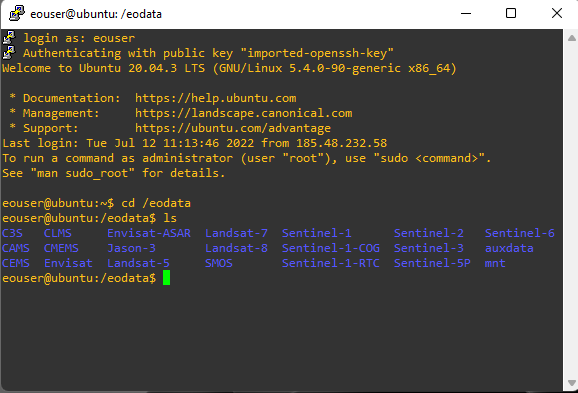
If you successfully logged in to your ubuntu you are able to see eodata files like below:
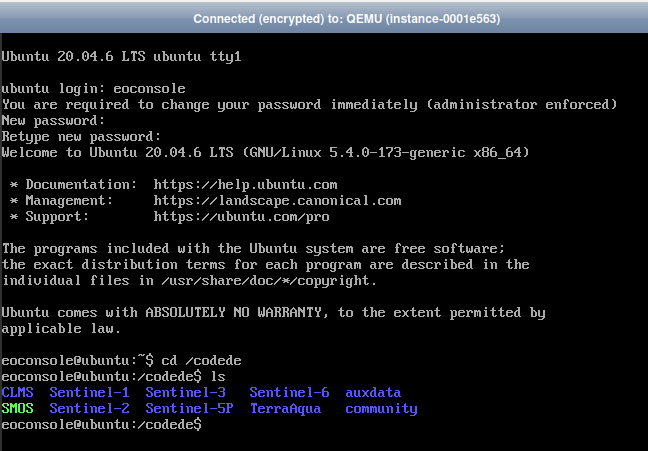
Step 4 Connect to your linux vm via ssh using putty.
First thing that is necessary, you must convert your private key to putty format.
If you have Putty installed, you also have application called PuttyGen open it and import your saved key.
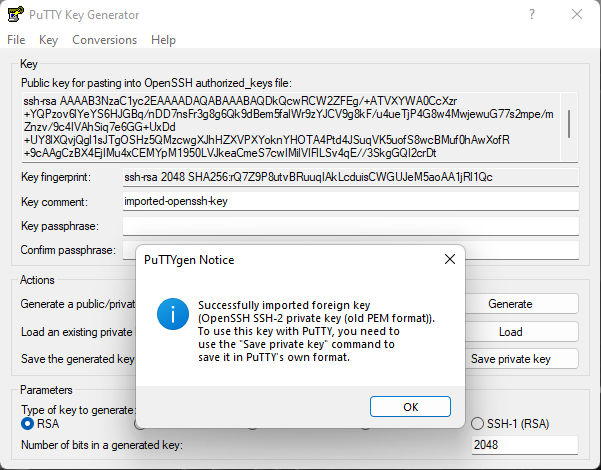
If everything is right you should see window like this. Confirm and then click save private key.
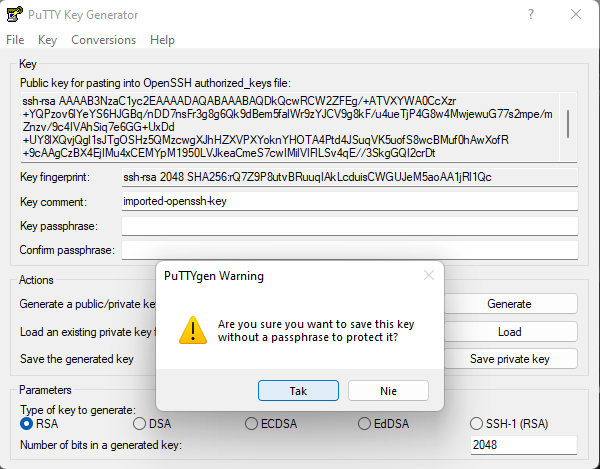
Confirm and save your key wherever you want.
Open putty app and in the field Host Name (or IP address) type your floating (public) IP address.
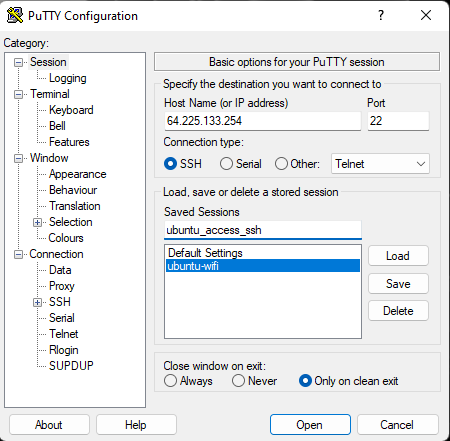
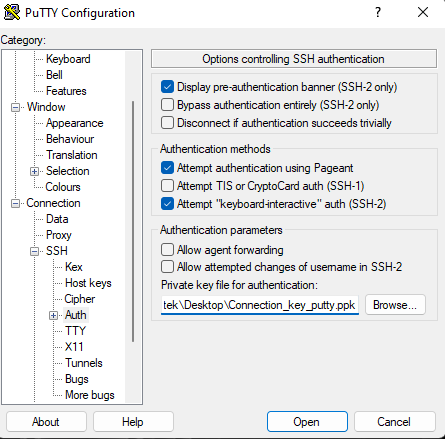
Then go to Connection→SSH→ Auth and Browse your key in putty format.
Go to Session, name your session and click save. I named it: ubuntu_access_ssh.
If you trying to connect for the first time you should see something like this:
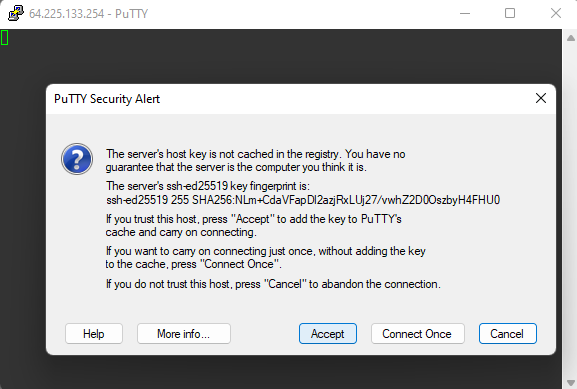
Confirm it and login as eouser, then you are successfully connected to your vm via ssh and Putty.